Easy as 2, 3, 4Find all x between 0 and 90 degrees that satisfy the equation
sin(2x) + tan(3x) + cos(4x) = 2Read more...
sin(2x) + tan(3x) + cos(4x) = 2
Logs Within LogsFind the value of n if:
log2(log3(log42n)) = 2Read more...
log2(log3(log42n)) = 2
Fractional SystemSolve the system of equations in positive real a,b,c:
ab + ba + ac + ca + bc + cb = 6
abc + bac + cab = 4
Please note: A complete solution must demonstrate that you have all possible solutions!Read more...
Please note: A complete solution must demonstrate that you have all possible solutions!
A Recursive Partitioned FunctionConsider a function, f(n), defined recursively by parts:
f(n+1) = f(n) + 3 while f(n) f(n+1) = f(n) - 2 while f(n) > 100
f(1) = 50
Find the value of f(500).Read more...
f(n+1) = f(n) + 3 while f(n) f(n+1) = f(n) - 2 while f(n) > 100
f(1) = 50
Find the value of f(500).
Analytic Trigonometry
Lines a1 and a2 in two-space intersect at a point, forming an acute angle A. The slope of a1 is √3, and cos A = 1/7. What is the slope of a2? Please note: all answers must be in exact radical form.
Read more...
Lines a1 and a2 in two-space intersect at a point, forming an acute angle A. The slope of a1 is √3, and cos A = 1/7. What is the slope of a2? Please note: all answers must be in exact radical form.
ConicsUsing the definition of a hyperbola, rotate the conic section defined by the equation
((x-3)3)2 - ((y-1)4)2 = 1
45 degrees counterclockwise about its center.
Express your equation in the form Ax2 + Bxy + Cy2 + Dx + Ey + F = 0, where the coefficients A through F are relatively prime integers. You will not need to belabor your process of simplification - please, however, describe the steps you take to simplify.Read more...
(
45 degrees counterclockwise about its center.
Express your equation in the form Ax2 + Bxy + Cy2 + Dx + Ey + F = 0, where the coefficients A through F are relatively prime integers. You will not need to belabor your process of simplification - please, however, describe the steps you take to simplify.
Literal Equationsax + by = c
ax2 + by2 = c
d
xy
Find the minimum value of a + b, assuming all variables are positive.Read more...
ax2 + by2 = c
d
xy
Find the minimum value of a + b, assuming all variables are positive.
Pythagorean TriplesA little more fun with Pythagorean triples:
Exactly four right triangles with integer side lengths exist with a leg equal to 15. These are:
(15, 112, 113), (15, 20, 25), (15, 36, 39), and (8, 15, 17).
How many different right triangle with integer side lengths exist with a leg equal to 42? How do you know?
BONUS QUESTION:
42 is the product of 3 different prime numbers - 2, 3, and 7.
Resolve this problem given a leg which is the product of n different primes, given that, as in this problem, one of these primes is 2.Read more...
Exactly four right triangles with integer side lengths exist with a leg equal to 15. These are:
(15, 112, 113), (15, 20, 25), (15, 36, 39), and (8, 15, 17).
How many different right triangle with integer side lengths exist with a leg equal to 42? How do you know?
BONUS QUESTION:
42 is the product of 3 different prime numbers - 2, 3, and 7.
Resolve this problem given a leg which is the product of n different primes, given that, as in this problem, one of these primes is 2.
Theorem of Pappus
The Theorem of Pappus states that when a region R is rotated about a line l, the volume of the solid generated is equal to the product of the area of R and the distance the centroid of the region has traveled in one full rotation. The centroid of a region is essentially the one point on which the region should "balance." The centroid of a rectangle with vertices (0,0), (x,0), (0,y), and (x,y) is the point (x/2,y/2), for example, but finding the centroid of a non-rectangular region is a little bit trickier. Part of this week's problem will require you to come up with a unique way of locating the centroid of a semicircle.
Consider the figure below, a rectangle topped by a semicircle.
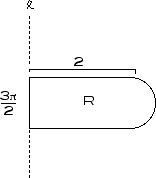

Use the Theorem of Pappus to:
1) Find the centroid of the semicircle and use it to find the volume of the solid generated when just the semicircle is rotated about l.
2) Find the volume of the solid generated when just the rectangle is rotated about l.
3) Find the distance from the centroid of the region R to l.
Read more...
The Theorem of Pappus states that when a region R is rotated about a line l, the volume of the solid generated is equal to the product of the area of R and the distance the centroid of the region has traveled in one full rotation. The centroid of a region is essentially the one point on which the region should "balance." The centroid of a rectangle with vertices (0,0), (x,0), (0,y), and (x,y) is the point (x/2,y/2), for example, but finding the centroid of a non-rectangular region is a little bit trickier. Part of this week's problem will require you to come up with a unique way of locating the centroid of a semicircle.
Consider the figure below, a rectangle topped by a semicircle.


Use the Theorem of Pappus to:
1) Find the centroid of the semicircle and use it to find the volume of the solid generated when just the semicircle is rotated about l.
2) Find the volume of the solid generated when just the rectangle is rotated about l.
3) Find the distance from the centroid of the region R to l.
Theorem of Pappus: Continued
Soroban noticed that the final answer to last week's problem, 9π2 + 323π2 + 32, is very close to 2, which is the length of the rectangle. (You may want to look over last week's solution.)
Is there some height h of a rectangle of length 2 such that a semi-circular "cap" will move its centroid exactly one unit to the right? If so, find it.


Read more...
Is there some height h of a rectangle of length 2 such that a semi-circular "cap" will move its centroid exactly one unit to the right? If so, find it.


An infinite color spectrum in a bottomless pitThere are x beads in a bottomless pit. Only two of them are the same color. Two beads are chosen at random. Let p(x) equal the probability that these two beads are the same color. Find
∞Σp(x)X=3Read more...
* Operations and Matrices
"*" operates as follows:
a*b = a + (b2 - ab)(a-b)
"#" operates as follows:
n# = n*([n-1]*([n-2]*...*(3*(2*1))))
Given that


what are the value(s) of x and y?
Read more...
a*b = a +
"#" operates as follows:
n# = n*([n-1]*([n-2]*...*(3*(2*1))))
Given that


what are the value(s) of x and y?
Inequalities and Geometric Similarities


Given:
AB = 4x
BC = x + 2
AC = x + 4
CD = 3x + 10
AD = 12
Find the range of values of x such that the area of triangle ABC exceeds that of triangle ACD.
Read more...


Given:
AB = 4x
BC = x + 2
AC = x + 4
CD = 3x + 10
AD = 12
Find the range of values of x such that the area of triangle ABC exceeds that of triangle ACD.
A Volume Problem


In triangle ABC, AB = 25, BC = 16, and AC = 39. If ABC is rotated about its shortest side, what is the volume of the resultant solid?
Read more...


In triangle ABC, AB = 25, BC = 16, and AC = 39. If ABC is rotated about its shortest side, what is the volume of the resultant solid?
A Recursive SequenceA sequence u is defined recursively as follows:
u0 = 4
u1 = 7
un+2 = 5un+1 - 6un for all n>=2.
Find the value of ux for all x>=2. Your answer should be a function of x.Read more...
u0 = 4
u1 = 7
un+2 = 5un+1 - 6un for all n>=2.
Find the value of ux for all x>=2. Your answer should be a function of x.
